Rheumatoid Arthritis: Navigating Life with a Chronic Condition
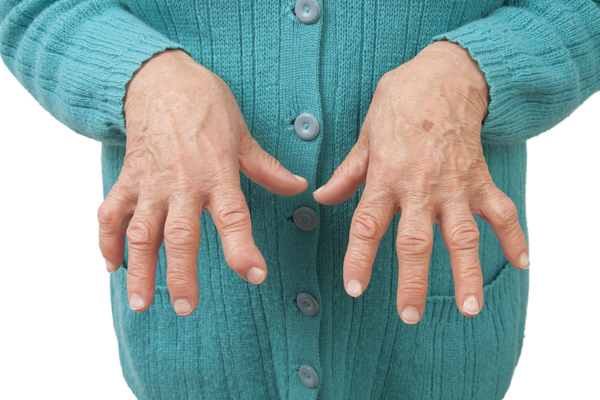
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by inflammation of the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling, which can significantly impact one&8217;s lifestyle. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the multifaceted aspects of living with rheumatoid arthritis, exploring its effects on physical health, emotional well-being, and everyday activities, as well as discussing strategies for managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Living with rheumatoid arthritis often entails navigating a complex array of physical symptoms that can vary in severity and fluctuate over time. Joint pain and stiffness are hallmark features of RA, often most pronounced in the morning or after periods of inactivity, making it challenging to engage in daily tasks and activities. The inflammation associated with RA can also lead to joint swelling and tenderness, further limiting mobility and causing discomfort. Over time, the progressive nature of the disease can result in joint damage and deformity, posing additional challenges for individuals striving to maintain independence and functionality in their daily lives.
Beyond the physical manifestations, rheumatoid arthritis can also take a toll on emotional well-being, impacting mental health and overall quality of life. The chronic nature of the condition, coupled with its unpredictable course and fluctuating symptoms, can contribute to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and depression. Coping with chronic pain and disability can also lead to a sense of loss and grief for the life one had envisioned, as well as feelings of isolation and social withdrawal. Moreover, the pervasive nature of RA can disrupt various aspects of life, including work, relationships, and leisure activities, further exacerbating emotional distress and impacting one&8217;s sense of identity and self-worth.
Despite the challenges posed by rheumatoid arthritis, there are various strategies and lifestyle modifications that individuals can implement to better manage their condition and improve their overall well-being. Adopting a comprehensive treatment plan, including medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes, is essential for controlling inflammation, managing symptoms, and preventing joint damage. Non-pharmacological interventions, such as regular exercise, joint protection techniques, and stress management strategies, can also play a crucial role in enhancing physical function and reducing pain and stiffness.
Furthermore, making adjustments to daily routines and environments can help individuals with RA conserve energy, minimize strain on affected joints, and optimize functionality. This may involve incorporating assistive devices and adaptive equipment into daily activities, such as ergonomic tools, braces, and mobility aids, to facilitate independence and alleviate discomfort. Additionally, modifying home and work environments to improve accessibility and reduce physical barriers can enhance safety and promote greater autonomy for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis.
In addition to addressing the physical aspects of the condition, it is equally important to prioritize self-care and attend to emotional and psychosocial needs. Building a strong support network of family, friends, and healthcare professionals can provide invaluable encouragement, understanding, and assistance in coping with the challenges of living with RA. Participating in support groups or seeking counseling can also offer opportunities for emotional expression, peer support, and practical coping strategies for managing the emotional impact of the disease.
Moreover, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as maintaining a balanced diet, getting adequate rest, and practicing relaxation techniques, can support overall health and well-being in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Consuming a nutrient-rich diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids, can help reduce inflammation and support joint health. Prioritizing quality sleep and practicing stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga, can also help alleviate pain, improve mood, and enhance overall resilience in the face of chronic illness.
In conclusion, living with rheumatoid arthritis presents unique challenges that can impact various aspects of daily life, from physical function to emotional well-being. However, with a comprehensive approach to management that encompasses medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and psychosocial support, individuals with RA can achieve better symptom control, improved functionality, and enhanced quality of life. By adopting proactive strategies for self-care, engaging in supportive relationships, and making adjustments to daily routines and environments, individuals can navigate the complexities of rheumatoid arthritis with resilience, optimism, and a sense of empowerment.
